一.? ?概述
手骨識(shí)別應(yīng)用(Hand Skeleton Detection) 或是 手部特徵偵測(Hand Landmarks Detection) 是深度學(xué)習(xí)熱門的研究項(xiàng)目之一。主要用途是讓機(jī)器定位出手部的關(guān)節(jié)位置,並將各個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)連接起來。能夠廣泛應(yīng)用於手勢識(shí)別中,像是利用手勢來操作螢?zāi)唬蚴遣僮鲀x器時(shí)判斷手部姿勢是否正確。最常見的莫過於 Hand Landmarks 模組架構(gòu),也是利用 輕量化網(wǎng)路架構(gòu) MobileNet 作主幹,來達(dá)到模組輕量化的目的。
?
若新讀者欲理解更多人工智慧、機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)以及深度學(xué)習(xí)的資訊,可點(diǎn)選查閱下方博文
?大大通精彩博文???【ATU Book-i.MX8系列】博文索引
?
 ?
?
TensorFlow Lite 進(jìn)階系列博文-文章架構(gòu)示意圖
?
二.? 算法介紹
MobileNet 神經(jīng)網(wǎng)路架構(gòu) :
此架構(gòu)仍是使用 MobileNet 作為骨幹核心,其概念是利用拆分的概念,將原本的卷積層拆成 深度卷積(Depthwise Convolution) 與 逐點(diǎn)卷積(Pointwise Convolution) 兩個(gè)部分,稱作 深層可分離卷積(Depthwise Separable Convolution) 。以此方式進(jìn)行運(yùn)算,能夠大幅度減少參數(shù)量,以達(dá)到加快運(yùn)算速度。(用途擷取特徵)
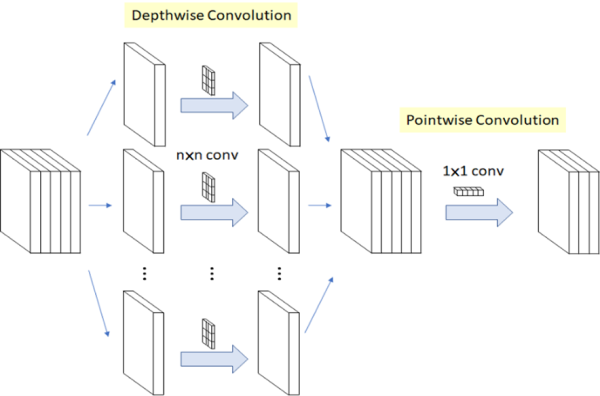
MobileNet 輕量化概念示意圖
圖文來源 -?參考 LaptrihnX 網(wǎng)站
?
Hand Skeleton Detection
此技術(shù)大致上可以分成 2D 與 3D 特徵點(diǎn)預(yù)測。簡單來說,前者指得就是考慮平面的關(guān)係,後者則必須考慮到空間的影響。也就是當(dāng)擺出 C 形狀的手勢時(shí),平面概念可能容易識(shí)別不到手勢,若以空間概念去訓(xùn)練模組的話,識(shí)別手勢的機(jī)率也會(huì)相應(yīng)增加。因此有些模組或是算法,會(huì)利用時(shí)間維度上來增加識(shí)別率,但也擴(kuò)大輸入資料。因此,Google 團(tuán)隊(duì)提出了一套 2.5D 預(yù)測方式,以手腕處作為中心點(diǎn)來計(jì)算各個(gè)關(guān)節(jié)點(diǎn)的相對深度,近而達(dá)到類似 3D 效果,且僅需輸入單一影像即可,其概念如下圖,
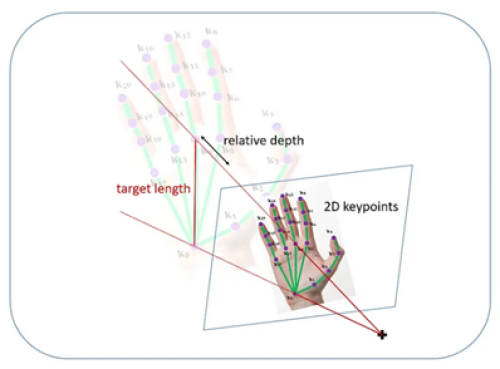
Hand Skeleton Detection 概念示意圖
圖文來源 -?Paper
?
同時(shí),該團(tuán)隊(duì)透過 3 萬張真實(shí)世界的圖片訓(xùn)練,來預(yù)測 21 個(gè)關(guān)節(jié)點(diǎn)的相對深度,如下圖。
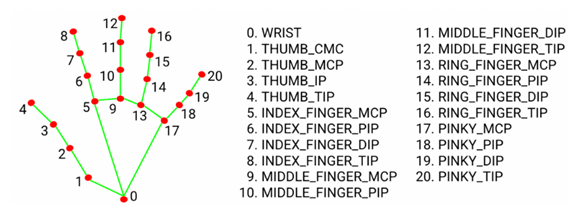
Hand Skeleton Detection各節(jié)點(diǎn)示意圖
圖文來源 -?參考MediaPipe 網(wǎng)站
?
二.? 算法介紹
Google 官方提供效果極佳的 Hand landmarks detection guide for Pytho 範(fàn)例與?Hand Landmark?模組實(shí)現(xiàn),讀者可直接依 MediaPiepe 的作法實(shí)現(xiàn)。而此範(fàn)例將延用該模組,並量化為整數(shù)運(yùn)算呈現(xiàn)。
實(shí)現(xiàn)步驟如下:
第一步 : 開啟 Colab 設(shè)定環(huán)境
%tensorflow_version 2.x第二步 : 下載轉(zhuǎn)換套件
!pip install tf2onnx
!pip install onnx-tf==1.9.0
!pip install onnx==1.9.0第三步 :? TensorFlow Lite 轉(zhuǎn)換 ONNX
! python -m tf2onnx.convert --opset 11 --tflite /root/hand_landmark.tflite --output /root/hand_landmark.onnx?
第四步 :? ONNX 轉(zhuǎn)換 SavedModel
! onnx-tf convert -i /root/hand_landmark.onnx -o /root/hand_landmark第五步 :? TensorFlow Lite 轉(zhuǎn)換
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def representative_dataset_gen():
for _ in range(250):
yield [np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0, size=(1, 256, 256, 3)).astype(np.float32)]
model = tf.saved_model.load("/root/hand_landmark")
concrete_func = model.signatures["serving_default"]
concrete_func.inputs[0].set_shape([1, 256, 256, 3])
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_concrete_functions([concrete_func])
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
converter.inference_input_type = tf.float32
converter.inference_output_type = tf.float32
converter.representative_dataset = representative_dataset_gen
tflite_model = converter.convert()
with open("/root/handskeleton_qunat_new.tflite",'wb') as f:
f.write(tflite_model)第六步 : Hand Skeleton Detection 範(fàn)例實(shí)現(xiàn) (於 i.MX8M Plus 撰寫運(yùn)行)
import sysimport cv2
import time
import argparse
import numpy as np
from tflite_runtime.interpreter import Interpreter
interpreter = Interpreter(model_path='/root/handskeleton_qunat_new.tflite')
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
width = input_details[0]['shape'][2]
height = input_details[0]['shape'][1]
nChannel = input_details[0]['shape'][3]
frame = cv2.imread("/root/hand.jpg")
frame_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
frame_resized = cv2.resize(frame_rgb, (width, height))
input_data = np.expand_dims(frame_resized, axis=0)
input_data = input_data.astype('float32')
input_data = input_data /255
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
interpreter_time_start = time.time()
interpreter.invoke()
interpreter_time_end = time.time()
print("Inference Time = ", (interpreter_time_end - interpreter_time_start)*1000 , " ms" )
feature = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index'])[0].reshape(21, 3)
hand_detected = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[1]['index'])[0]
# 建立輸出結(jié)果 - 特徵位置
Px = []
Py = []
size_rate = [frame.shape[1]/width, frame.shape[0]/height]
for pt in feature:
x = int(pt[0]*size_rate[0])
y = int(pt[1]*size_rate[1])
Px.append(x)
Py.append(y)
# 建立輸出結(jié)果
if (hand_detected) :
# 拇指
cv2.line(frame, (Px[0], Py[0]) , (Px[1], Py[1]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[1], Py[1]) , (Px[2], Py[2]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[2], Py[2]) , (Px[3], Py[3]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[3], Py[3]) , (Px[4], Py[4]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
# 食指
cv2.line(frame, (Px[0], Py[0]) , (Px[5], Py[5]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[5], Py[5]) , (Px[6], Py[6]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[6], Py[6]) , (Px[7], Py[7]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[7], Py[7]) , (Px[8], Py[8]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
# 中指
cv2.line(frame, (Px[5], Py[5]) , (Px[9], Py[9]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[9], Py[9]) , (Px[10], Py[10]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[10], Py[10]) , (Px[11], Py[11]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[11], Py[11]) , (Px[12], Py[12]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
# 無名指
cv2.line(frame, (Px[9], Py[9]) , (Px[13], Py[13]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[13], Py[13]) , (Px[14], Py[14]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[14], Py[14]) , (Px[15], Py[15]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[15], Py[15]) , (Px[16], Py[16]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
# 小指
cv2.line(frame, (Px[13], Py[13]) , (Px[17], Py[17]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[17], Py[17]) , (Px[18], Py[18]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[18], Py[18]) , (Px[19], Py[19]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[19], Py[19]) , (Px[20], Py[20]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.line(frame, (Px[17], Py[17]) , (Px[0], Py[0]) , (0, 255, 0), 3)
#指節(jié)
for i in range(len(Px)):
cv2.circle(frame, ( Px[i] , Py[i] ), 1, (0, 0, 255), 4)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
?
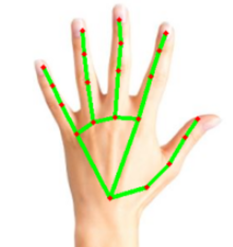
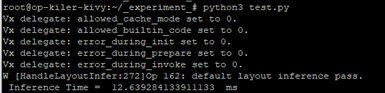
?Hand Skeleton Detection 實(shí)現(xiàn)結(jié)果呈現(xiàn)?
如下圖所示,成功將圖片轉(zhuǎn)換偵測到各個(gè)手部關(guān)節(jié)的位置。
在 i.MX8M Plus 的 NPU 處理器,推理時(shí)間(Inference Time) 約 12.69 ms。
?
四.? 結(jié)語
手骨識(shí)別應(yīng)用 (Hand Skeleton Detection) 通常需要搭配 手部偵測(Hand Detection) 來作應(yīng)用。也就是偵測到手部的位置後,將局部會(huì)特徵交付給手骨識(shí)別模組進(jìn)行特徵提取,才能將準(zhǔn)確度應(yīng)用最大化。最後利用所檢測到的 21 個(gè)手骨關(guān)節(jié)位置來作後續(xù)的判斷機(jī)制,即可以實(shí)現(xiàn)手勢操作等等應(yīng)用。目前運(yùn)行在 i.MX8MP 的 Vivante VIP8000 NPU,其推理時(shí)間可達(dá)每秒 12.69 ms 的處理速度,約 78 張 FPS ,以及在適當(dāng)?shù)木嚯x下,有不錯(cuò)的檢測率。 由於此範(fàn)例屬於複合式的應(yīng)用,故實(shí)際花費(fèi)時(shí)間應(yīng)該為手部與手骨偵測的花費(fèi)時(shí)間,粗估計(jì)算為 10ms + N * ( 12 ms ) ,其中? N 為偵測到的手部數(shù)量。下一章節(jié)將會(huì)介紹機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí) GAN 架構(gòu)應(yīng)用之一的 “風(fēng)格轉(zhuǎn)換應(yīng)用( Style Transform)” ,敬請期待 !!。
?
五.??參考文件
[1] SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector
[2] SSD-Tensorflow
[3] Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) 論文閱讀
[4] ssd-mobilenet v1 演算法結(jié)構(gòu)及程式碼介紹
[5] Nonparametric Structure Regularization Machine for 2D Hand Pose Estimationr
[6]Mediapipe - Hand landmarks detection guide for Python
如有任何相關(guān)?TensorFlow Lite?進(jìn)階技術(shù)問題,歡迎至博文底下留言提問?!!
接下來還會(huì)分享更多?TensorFlow Lite?進(jìn)階的技術(shù)文章?!!敬請期待?【ATU Book-i.MX8系列?– TFLite?進(jìn)階】?!!

參考來源